Hosted by: German Jordanian University, SABE (Amman, Jordan)
Funded by: DAAD
Locating and dimensioning spatial objects and with it the creation of spaces is at the heart of urban design. Thereby it is necessary to precast the effects that design decisions have on the behavior of the future users as well as to estimate the sustainability and resilience of the city. Computational analysis methods can help to support this process due to the fact that they can reveal properties that are hardly recognizable at first intuitive sight.
This workshop is a part of 10 days excursion in the city of Amman, Jordan. It will be the final stage of a seminar to learn and apply methods for the quantitative analysis of urban space (such as density, accessibility, visibility) and examine in how far these quantities relate to real life phenomena such as the spatial configuration of economical activities in a city or the movement patterns of urban users.
The seminar is part of an ongoing DAAD-funded project on discovering urban social and spatial patterns of Islamic cities and fostering exchange between German and Jordan academics in the field of urban planning.
Presentation
Workshop files
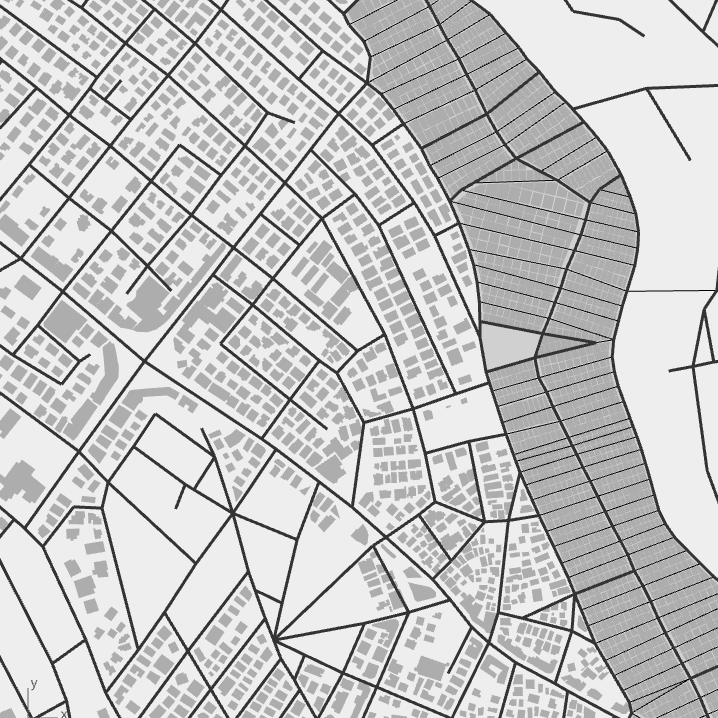
Jabal Al Hussain | model
Simplified street network and building footprints for Jabal Al Husain neighborhood.
Layers:
Palestinian refugee camp
- Pedestrian street network
- Car street network
- Building footprints
Jordanian old district
- Pedestrian street network
- Car street network
- Building footprints

Building coverage Density | script
Building coverage density is a measure of the relationship between built area (B) and area of the plan (A). It identifies how developed an area is along a scale of zero (no development) to one (the whole area is occupied by buildings).
This script measures the distribution of building coverage density through out the space and map the results on a grid. The plan area (A) in this script is defined as circular radius with flexible diameter parameter. The setting of the diameter influence if the density captures just close surrounding area of given location or larger neighborhood.

Street Network Centrality | script
Centrality measures for the street network in pedestrian radius of 600m and global car radius Rn. The analysis is calculated for Jordanian neighborhood alone and combined with the refugee camp
Centrality measures:
- Closeness (integration) R600, Rn
- Betweenness (choice) R600, Rn

Behaviour vs. Centrality | script
In this script you can link the empirical countings to the street network centrality and visualize the relationship between those two variables.The strong relationship suggest that the countings are influenced by the street network configuration. if not, they are independent.

